Better Money and Financial Management
Jump to sections on this page: Personal Finance Strategy and Management – A Synthesis – — Your Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Personal Financial Plan —- 7 Money Truths That Will Reshape Your Financial Future —- Your First Map to Financial Freedom: A Guide for Young Adults ——- Personal Finance Strategy and Management
We have a “Deep Dive” podcast on the subject the Chair Man and the Chair Lady. Listen on any device, CLICK PLAY.
Personal Finance Strategy and Management: A Synthesis
Personal Finance Strategy and Management: A Synthesis
Summary
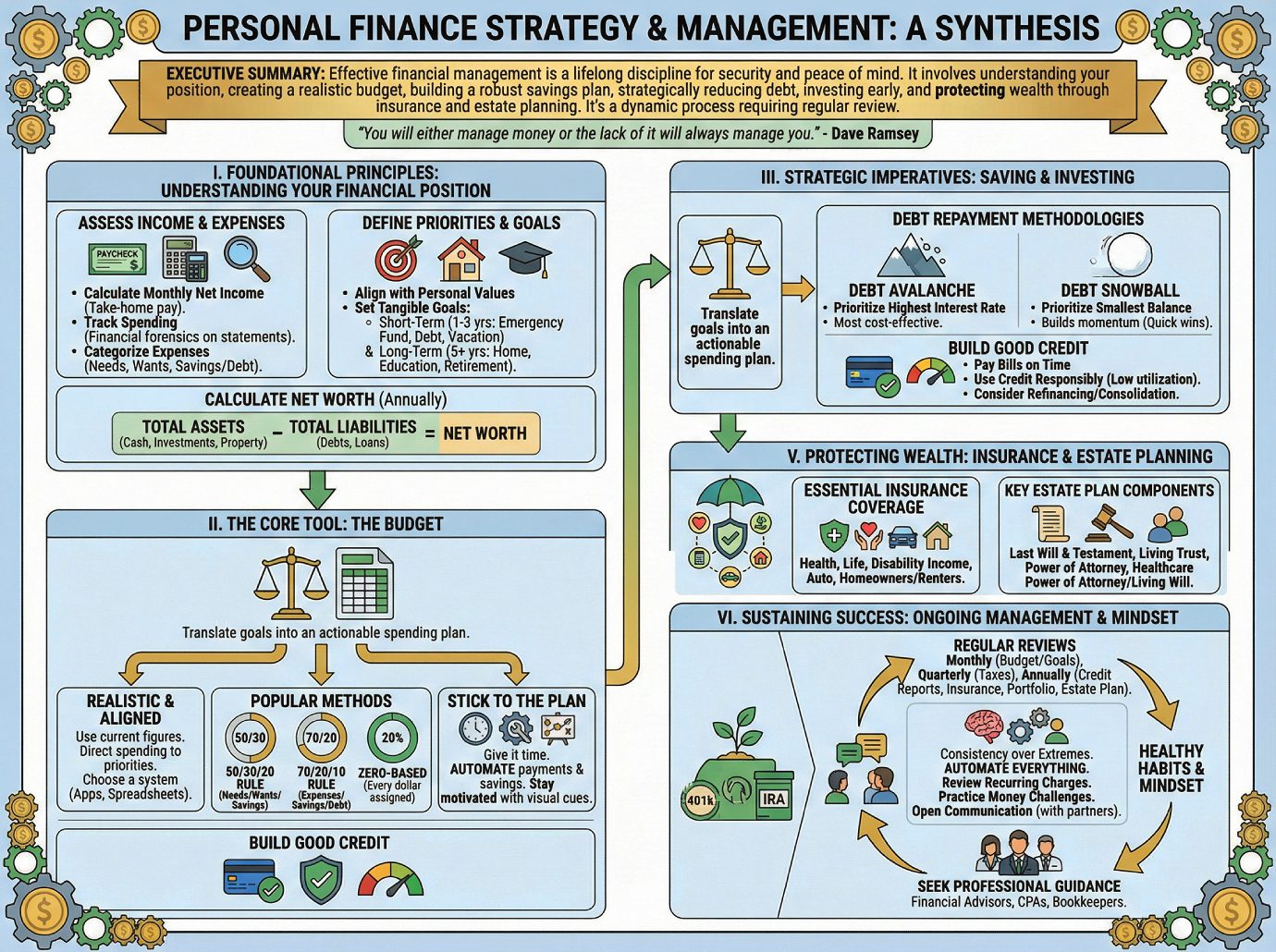
Effective personal financial management is a critical, lifelong discipline essential for achieving financial security and peace of mind. A comprehensive analysis of financial guidance reveals a consistent, multi-stage framework for success. The process begins with a foundational understanding of one’s complete financial picture—meticulously tracking all income sources and expenditures to calculate net worth and define personal priorities.
The primary tool for financial control is a realistic, consistently maintained budget, which aligns spending habits with strategic goals. Key among these goals is the creation of a robust savings plan, prioritizing an accessible emergency fund equivalent to three to six months of living expenses to buffer against unexpected events. Concurrently, a strategic approach to debt reduction, utilizing methods such as the “avalanche” or “snowball” techniques, is vital for freeing up capital and improving financial health.
For long-term wealth creation, early and consistent investment is paramount, particularly through tax-advantaged retirement vehicles like 401(k)s and IRAs, and capitalizing on employer matching programs. Finally, wealth must be protected through adequate insurance coverage and comprehensive estate planning. This entire process is dynamic; it requires regular reviews and adjustments to adapt to life events and evolving goals, ensuring sustained financial well-being. As financial expert Dave Ramsey states, “You will either manage money or the lack of it will always manage you.”
——————————————————————————–
I. Foundational Principles: Understanding Your Financial Position
Before any financial plan can be effective, a thorough and honest assessment of one’s current financial situation is required. This stage is about gathering data to create an accurate snapshot of financial health, which serves as the baseline for all subsequent planning and decision-making.
Assessing Income and Expenses
The first step is to gain a clear understanding of cash flow by determining monthly income and tracking all expenditures.
• Calculate Monthly Income: Determine total monthly take-home pay (net income) after taxes. This should include income from primary employment, side gigs (freelance work, ad revenue), and any other regular sources. For those with variable income, such as freelancers, an average or estimated monthly income should be calculated.
• Track Spending: Conduct a “financial forensics” on personal spending habits. This involves collecting and analyzing at least one month’s worth of financial records, including:
◦ Credit card and bank statements
◦ Housing and utility bills
◦ Records of electronic payments (Venmo, PayPal)
◦ ATM withdrawal records
• Categorize Expenses: As expenses are tallied, they should be grouped into categories. This can be a simple breakdown of “needs,” “wants,” and “savings/debt,” or a more detailed list including categories like housing, transportation, food, entertainment, and travel. This categorization reveals where the bulk of income is directed.
Calculating Net Worth
Understanding net worth provides a holistic view of one’s financial standing at a specific point in time. It should be calculated annually to track progress.
| Component | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Assets | Everything owned that has monetary value. | Cash, checking/savings accounts, investments, home equity, vehicles. |
| Liabilities | All outstanding debts and financial obligations owed to others. | Mortgages, car loans, student loans, credit card balances. |
| Net Worth | Total Assets – Total Liabilities | A positive figure indicates owning more than is owed. |
Defining Financial Priorities and Goals
With a clear financial picture, the next step is to define priorities and set specific, measurable goals. This crucial step provides motivation and direction for a financial plan.
• Align with Personal Values: As personal finance authority Patrice Washington advises, money priorities should align with personal values. “The largest categories should reflect what matters most to you,” whether that is travel, fitness, or family.
• Set Tangible Goals: Financial goals should be specific, with numbers and dates attached. They can be broken down into two main categories:
◦ Short-Term Goals (1-3 years): Building an emergency fund, paying off high-interest credit card debt, saving for a vacation, or making a down payment on a vehicle.
◦ Long-Term Goals (5+ years): Saving for a home down payment, funding a child’s education, starting a business, building wealth, or planning for retirement.
II. The Core Tool: The Budget
A budget is the central planning document that translates financial goals into an actionable spending plan. It is not merely a restrictive tool but a guide for allocating resources effectively to achieve desired outcomes.
Creating a Realistic Budget
An effective budget must be based on the accurate income and expense data gathered in the foundational stage.
1. Use Realistic Figures: The budget should reflect finances as they currently are, not as one wishes them to be.
2. Align with Priorities: The plan should direct spending toward the priorities identified in the goal-setting phase. For example, if establishing an emergency fund is the top priority, the budget must allocate funds to a dedicated savings account by reducing spending in lower-priority areas.
3. Choose a System: Select a budgeting system that is easy to maintain. Options include:
◦ Simple spreadsheets
◦ Dedicated budgeting apps (e.g., Mint, You Need a Budget (YNAB), Quicken, Goodbudget)
◦ Pen and paper
Popular Budgeting Methods
Several established frameworks can guide the creation of a budget.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| 50/30/20 Rule | 50% of take-home pay is allocated to Needs (housing, utilities, groceries). 30% is allocated to Wants (entertainment, dining out). 20% is allocated to Savings and Debt Repayment. |
| 70/20/10 Rule | 70% of take-home pay is for Expenses. 20% is for Savings. 10% is for Debt Repayment. |
| Zero-Based | Every dollar of income is assigned a specific purpose (spending, saving, debt), leaving a balance of zero. |
Sticking to the Plan
Consistency is the key to a successful budget.
• Give it Time: A new budget should be tested for at least one full month to determine its effectiveness and sustainability.
• Automate: Set up automatic bill payments and savings transfers. This ensures priorities are met before money can be spent elsewhere.
• Stay Motivated: Use visual cues to maintain focus. Patrice Washington recommends surrounding oneself with “visual representations” of goals, such as pictures of a dream vacation destination.
III. Strategic Imperatives: Saving and Investing
Once a budget is in place, the focus shifts to building financial security and growing wealth through disciplined saving and strategic investing.
Building an Emergency Fund
An emergency fund is a liquid cash reserve for major, unexpected expenses (e.g., job loss, medical emergencies, major car repairs). It is a critical financial safety net.
• Target Amount: The standard recommendation is to save three to six months of essential living expenses.
• Starter Fund: For those starting out, a more achievable initial goal is a $1,000 starter emergency fund. A recent survey noted that 25% of respondents had no emergency savings at all.
• Accessibility: These funds should be kept in a high-yield savings account where they are easily accessible but separate from regular checking accounts to avoid casual spending.
Saving for Goals
Beyond emergencies, savings should be directed toward specific short-term and long-term goals. Using separate, dedicated savings accounts for different goals (e.g., “Vacation Fund,” “New Car Fund”) can improve organization and motivation.
Retirement Planning and Investment Strategies
Saving for retirement should begin as early as possible to maximize the power of compound interest.
• Employer-Sponsored Plans (401k): If an employer offers a 401(k) matching program, contributing enough to receive the full match is essential. This is often described as “free money.”
• Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs): IRAs (Traditional or Roth) are powerful, tax-advantaged tools for retirement savings, available to those with or without an employer plan.
• Investing Fundamentals:
◦ Risk Tolerance: Understand your personal comfort level with market fluctuations.
◦ Diversification: Spread investments across various asset classes (stocks, bonds) to manage risk.
◦ Consistency: Invest regularly, even small amounts. Don’t try to time the market by jumping in and out.
◦ Accessibility: Financial apps and robo-advisors like Wealthfront and Betterment have made investing more accessible for beginners.
IV. Managing Liabilities: Debt and Credit
Effectively managing and reducing debt is crucial for financial progress, as high-interest payments can significantly hinder the ability to save and invest.
Debt Repayment Methodologies
Two primary strategies exist for paying down debt. The choice depends on whether mathematical efficiency or psychological motivation is a higher priority.
| Method | Approach | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Debt Avalanche | Prioritize paying off debts with the highest interest rates first, while making minimum payments on others. | Most cost-effective; minimizes total interest paid. | May take longer to see the first debt eliminated. |
| Debt Snowball | Prioritize paying off debts with the smallest balances first, regardless of interest rate. | Provides quick wins and builds momentum/confidence. | May result in paying more total interest over time. |
Refinancing and Consolidation
Regularly review existing debt to identify opportunities for savings. This can include:
• Refinancing mortgages, auto loans, or student loans to secure a lower interest rate.
• Consolidating multiple debts into a single personal loan with a lower interest rate.
• Transferring high-interest credit card balances to a card with a lower introductory or promotional interest rate.
Building and Maintaining Good Credit
A strong credit history is essential for accessing future loans at favorable rates. Responsible financial habits are key.
• Pay Bills on Time: This is a fundamental component of a good credit score.
• Use Credit Responsibly: Open credit cards and use them responsibly by making on-time payments and maintaining a low credit utilization rate.
V. Protecting Wealth: Insurance and Estate Planning
Building wealth is only part of the equation; protecting it from unforeseen events is equally important. This involves having adequate insurance and a comprehensive estate plan.
Essential Insurance Coverage
Insurance acts as a safeguard against catastrophic financial loss. Key types include:
• Health Insurance: Protects against high medical costs.
• Life Insurance: Provides financial support for dependents.
• Disability Income Insurance: Replaces a portion of income if one is unable to work due to illness or injury.
• Auto Insurance: Covers expenses related to vehicle accidents.
• Homeowners or Renters Insurance: Protects property and personal belongings.
Key Components of an Estate Plan
Estate planning ensures assets are distributed according to one’s wishes and that personal affairs are handled in case of incapacitation.
• Last Will and Testament: A legal document outlining how assets should be distributed and naming guardians for minor children.
• Living Trust: Can help heirs avoid the potentially lengthy and costly probate process.
• Power of Attorney: Designates a trusted individual to make financial decisions on your behalf if you become unable to do so.
• Healthcare Power of Attorney / Living Will: Outlines preferences for medical treatment and designates someone to make healthcare decisions on your behalf.
VI. Sustaining Success: Ongoing Management and Mindset
Personal finance is a dynamic, ongoing process that requires regular attention and a disciplined mindset.
The Importance of Regular Financial Reviews
A “set it and forget it” mindset does not work for personal finance. Schedule regular check-ins to stay on track.
• Monthly: Review the budget and track progress toward goals.
• Quarterly: Check on tax deadlines if applicable.
• Annually:
◦ Review credit reports from all three major bureaus (Equifax, Experian, TransUnion).
◦ Re-evaluate insurance coverage.
◦ Review investment portfolio and rebalance if necessary.
◦ Meet with a financial professional.
◦ Update estate planning documents after major life events (marriage, birth of a child, etc.).
Behavioral Finance and Healthy Habits
Mindset and behavior are as important as the numbers.
• Consistency over Extremes: Drastic “crash diet” approaches to finance are often unsustainable. Small, consistent changes, like reducing spending by 10%, are more effective.
• Automate Everything: Automate savings, investments, and bill payments to remove friction and the temptation to spend.
• Review Recurring Charges: Scrutinize bank statements for subscriptions and memberships that are no longer used. Research found that forgotten subscriptions cost consumers £1.6 billion a year.
• Practice Money Challenges: Short-term challenges like a “no-spend month” or the “1p challenge” (saving an additional penny each day) can build savings habits in an engaging way.
• Open Communication: For those with partners, regular, open conversations about money are crucial for aligning goals and building a shared financial future.
Seeking Professional Guidance
Financial matters can be complex. Working with professionals can provide up-to-date, personalized guidance. Consider consulting with:
• Financial Advisors: For comprehensive financial planning and investment management.
• Certified Public Accountants (CPAs): For tax planning and preparation.
• Bookkeepers: For managing day-to-day business finances.
—————————————————————————————————————–
Your Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Personal Financial Plan
Your Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Personal Financial Plan
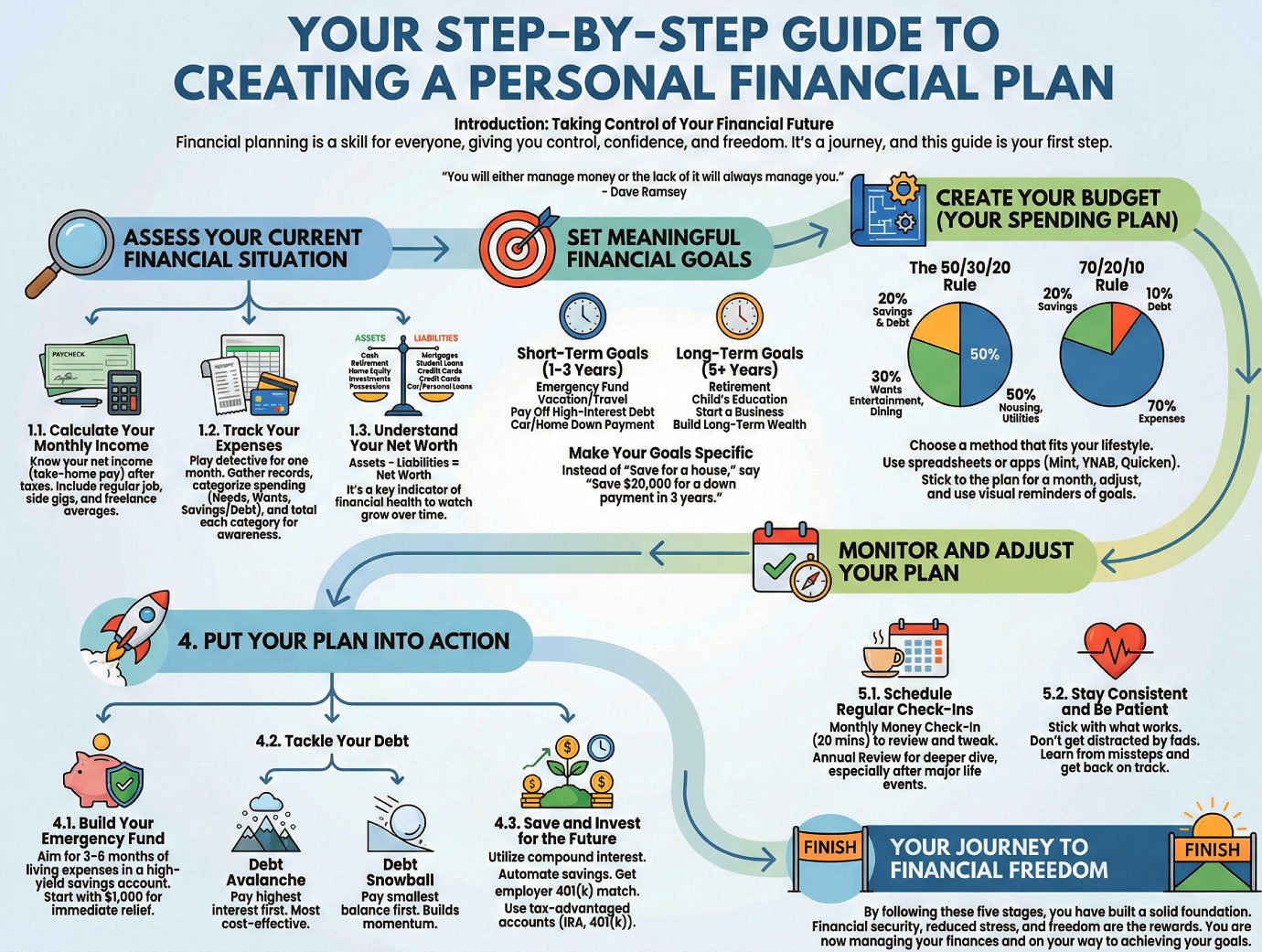
Introduction: Taking Control of Your Financial Future
Welcome! If the idea of “financial planning” sounds intimidating or like something reserved for the wealthy, I’m here to tell you that it’s simply a skill—one that anyone can learn. Managing your money is about giving yourself control, confidence, and the freedom to pursue your dreams. It’s a journey, and this guide is your first step.
“You will either manage money or the lack of it will always manage you.” — Dave Ramsey
Creating a financial plan is a powerful way to align your daily habits with your life goals. We will walk through five key stages to build your plan: assessing your finances, setting goals, creating a budget, putting the plan into action, and monitoring your progress.
Let’s begin with the first crucial step: getting a clear and honest picture of where you stand financially today.
——————————————————————————–
1. Stage 1: Assess Your Current Financial Situation
This first stage is about creating a clear snapshot of your financial life. You can’t plan a route without knowing your starting point.
1.1. Calculate Your Monthly Income
The first piece of the puzzle is knowing exactly how much money you have coming in each month after taxes. This is often called your net income or take-home pay.
• Start with your paycheck: If you have a regular job, this is the amount deposited into your bank account.
• Add any extra income: Include money you make from side gigs, like babysitting, ad revenue from a blog, or teaching a fitness class.
• For freelancers: If your income varies, you may need to estimate your average monthly income based on the past few months.
1.2. Track Your Expenses
Next, it’s time to play detective and figure out where your money is going. Tracking your spending for at least one full month gives you an accurate picture of your financial habits.
1. Gather Your Records: Pull together your credit card and bank statements, utility bills, and any records from electronic payment apps like Venmo or PayPal.
2. Categorize Your Spending: As you go through your records, group your expenses. A simple way to start is by labeling each expense as a “need,” “want,” or “savings/debt.” For more detail, you can create categories like “entertainment,” “groceries,” “transportation,” and “travel.”
3. Total Each Category: Add up the expenses in each category. This will show you where the bulk of your money is going, and the results might surprise you! Don’t judge what you find here. This isn’t about guilt; it’s about awareness. Gaining this clarity is a huge win and the first real step toward taking control.
1.3. Understand Your Net Worth (Assets vs. Liabilities)
Your net worth is a key indicator of your overall financial health. It’s calculated by taking the total value of what you own (your assets) and subtracting the total amount of what you owe (your liabilities). Don’t be discouraged if this number is low or negative at first. The goal isn’t to judge your past, but to give you a single, powerful number you can watch grow over time. It’s the ultimate measure of your financial progress.
| Assets (What you own) | Liabilities (What you owe) |
|---|---|
| Cash in checking/savings | Mortgages |
| Retirement accounts (401k, IRA) | Student loans |
| Home equity | Credit card balances |
| Investment accounts | Car loans |
| Valuable possessions | Personal loans |
Now that you have a complete snapshot of your current financial life, you are ready to set your sights on the future and define what you want to achieve.
——————————————————————————–
2. Stage 2: Set Meaningful Financial Goals
With a clear picture of your finances, you can now decide what you want to achieve. This is the “why” behind all your efforts. Without clear goals, a budget feels like a restriction. With them, it becomes a roadmap to your dreams.
2.1. Differentiate Between Short-Term and Long-Term Goals
Breaking your goals down by timeline makes them feel much more manageable. Don’t worry if a goal falls in the middle, like saving for a wedding in four years. These categories are just guidelines to help you organize your thoughts and prioritize.
• Short-term goals are things you want to achieve within the next 1-3 years.
• Long-term goals are bigger objectives that may take 5 years or more.
Here are some common examples to get you thinking:
• Examples of Short-Term Goals:
◦ Building an emergency fund
◦ Saving for a vacation or travel fund
◦ Paying off high-interest credit card debt
◦ Saving for a down payment for a car or home
• Examples of Long-Term Goals:
◦ Saving for retirement
◦ Paying for a child’s education
◦ Starting a business
◦ Building long-term wealth
2.2. Make Your Goals Specific
Vague goals are hard to act on. To make your goals powerful, attach specific numbers and dates to them. This transforms a wish into a concrete plan.
For example, instead of saying, “I want to save for a house,” a more specific and actionable goal would be, “I will save $20,000 for a down payment in the next 3 years.”
With your goals clearly defined, it’s time to build the practical tool that will help you reach them: your budget.
——————————————————————————–
3. Stage 3: Create Your Budget (Your Spending Plan)
A budget is simply a plan for your money. It’s the tool that turns your abstract goals into a concrete, daily reality, giving you permission to spend confidently on what you value. It’s the roadmap that aligns your spending with your goals, giving you control and confidence.
3.1. Choose a Budgeting Method
The best budget is one you can stick to, so don’t overcomplicate it. The key is to find a system that feels realistic for your lifestyle. Here are two popular rules to get you started:
| Budgeting Rule | How It Works |
|---|---|
| The 50/30/20 Rule | Divides take-home pay into three buckets: 50% for Needs (housing, utilities), 30% for Wants (entertainment, dining out), and 20% for Savings & Debt Repayment. |
| The 70/20/10 Rule | Divides take-home pay into three different buckets: 70% for Expenses, 20% for Savings, and 10% for Debt. |
You can manage your budget with a simple spreadsheet or use a budgeting app like Mint, YNAB, or Quicken. The right tool is whichever one you will use consistently.
3.2. Stick to the Plan
Give your chosen budget a trial run for at least one month. This gives you enough time to see what’s working and what might need adjusting.
To stay motivated, remember the specific, meaningful goals you set in Stage 2. As financial authority Patrice Washington suggests, “surround yourself with visual representations” of those goals. If your goal is to “save $20,000 for a down payment in 3 years,” put a picture of your dream home on your fridge. This transforms your budget from a set of rules into a daily reminder of the future you’re building.
Now that you have your plan, let’s move on to the most exciting part: putting it into action.
——————————————————————————–
4. Stage 4: Put Your Plan into Action
This is where your planning turns into progress. By taking these steps, you can start to protect your finances and grow your wealth.
4.1. Build Your Emergency Fund
An emergency fund is your financial safety net. It’s cash set aside for major, unexpected expenses like a medical bill, a major car repair, or a sudden job loss.
Experts recommend saving three to six months of living expenses in an easily accessible, liquid account, like a high-yield savings account.
If saving 3-6 months of expenses feels like trying to climb Mount Everest, focus on the first hill: $1,000. This single step provides an incredible amount of psychological relief and protects you from the tyranny of small emergencies.
4.2. Tackle Your Debt
Paying down debt, especially high-interest debt, frees up your money to work for your goals. There are two popular strategies for paying off debt:
| Method | Description | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Debt Avalanche | Pay off debts with the highest interest rates first, while making minimum payments on others. | Most cost-effective, as it reduces the total amount of interest paid over time. |
| Debt Snowball | Pay off the smallest debt balances first, regardless of interest rate, to build momentum. | Builds financial confidence and motivation through quick wins. |
4.3. Save and Invest for the Future
The sooner you start saving and investing, the more time your money has to grow, thanks to the power of compound interest. The most effective way to harness the power of compound interest—where your money starts earning its own money—is to automate your savings. By setting up automatic transfers, you ensure you’re consistently feeding your investment engine without relying on willpower. It’s the “set it and forget it” path to long-term wealth.
• Take Advantage of Free Money: If your employer offers a 401(k) match, contribute at least enough to get the full match. It’s one of the best returns on your money you can get.
• Use Retirement Accounts: Accounts like a 401(k) through your employer or an Individual Retirement Account (IRA) that you open on your own are powerful, tax-advantaged tools for long-term growth.
• Automate Your Savings: Make saving effortless by setting up automatic transfers from your checking account to your savings or investment accounts each payday.
Executing your plan is a huge accomplishment, but financial planning is a marathon, not a sprint. The final stage is about staying on course for the long haul.
——————————————————————————–
5. Stage 5: Monitor and Adjust Your Plan
A financial plan is a living document. Regularly checking in ensures it evolves with your life and keeps you on the path to success.
5.1. Schedule Regular Check-Ins
• Your Monthly Money Check-In: Pour a cup of coffee and spend 20 minutes with your budget. This isn’t about finding fault; it’s a chance to celebrate what worked, make small tweaks, and ensure you’re still on track. Catching things early keeps stress low.
• Annual Review: At least once a year, do a deeper dive into your overall financial plan. This is especially important after a major life event, such as getting married, having a child, or changing jobs.
5.2. Stay Consistent and Be Patient
As the saying goes, “if it’s not broke, don’t fix it.” Once you find a system that works for you, stick with it. Don’t get distracted by the latest financial fads if you are successfully saving money and meeting your goals.
Life can sometimes throw you off track, and that’s okay. A small misstep won’t ruin your long-term success. The most important thing is to acknowledge it, learn from it, and get right back on your budget.
——————————————————————————–
Conclusion: Your Journey to Financial Freedom
By following these five stages—assessing your situation, setting clear goals, creating a budget, taking action, and monitoring your progress—you have built a solid foundation for your financial future.
Personal finance is a journey of self-discipline, commitment, and continuous learning. But the rewards—financial security, reduced stress, and the freedom to live the life you want—are well worth the effort. By taking these steps, you are no longer letting your finances manage you; you are managing them. You are well on your way to achieving your goals.
—————————————————————-
7 Money Truths That Will Reshape Your Financial Future

7 Money Truths That Will Reshape Your Financial Future
Managing money often feels like a tricky, overwhelming subject, accompanied by a sense of apprehension and stress. For many, financial pressures are a significant source of worry, whether it’s putting off retirement savings, having no emergency cushion, or simply feeling like your finances are stuck in a bad place with no way out.
But achieving financial peace isn’t about mastering complex formulas or adopting extreme strategies. We’ve distilled the noise into seven core truths. Mastering them will give you more control than any complex spreadsheet, creating a clear path to the financial security you deserve.
——————————————————————————–
1. Your Budget Isn’t a Prison—It’s a Permission Slip for What You Value Most
Most people think of budgeting as a painful exercise in cutting back on spending. The reality is that an effective budget is not about restriction; it’s about intentional spending. The best financial plans align your money habits with your personal priorities and values.
As personal finance authority Patrice Washington advises, your budget should be a clear reflection of your priorities. A large travel category isn’t a flaw; it’s a choice. A significant wellness budget isn’t an overspend; it’s a value statement.
The largest categories should reflect what matters most to you.
This shift in perspective is powerful. It transforms budgeting from a negative chore focused on what you have to give up into a positive, empowering act of defining and funding the life you truly want to live.
2. You Must Be a Financial Detective Before You Can Be a CEO
Before you can act as the CEO of your finances, you must first serve as its lead detective. As the saying goes, “What gets measured, gets managed.” This “financial forensics” phase isn’t about judgment; it’s about gathering the critical intelligence you need to make profitable executive decisions later on.
The process is straightforward: take one month and review your bank statements, credit card bills, and records from payment apps like Venmo or PayPal. Tally up every expense to get a complete picture of your spending habits.
As you compile these expenses, organize them into categories like needs, wants, and savings/debt. You might be surprised by what you find—how much you really spend eating out or the percentage of your income that goes toward housing. This step is crucial because it provides the raw data needed to make informed, realistic decisions about your financial future.
3. There’s a ‘Right’ Way to Pay Off Debt (and It Depends on Your Brain, Not Just Your Math)
When it comes to paying off debt, there isn’t one single “right” way—there are two primary strategies, and the best one for you depends as much on psychology as it does on mathematics.
• The Debt Avalanche: This method involves paying off debts with the highest interest rates first while making minimum payments on all others. From a purely mathematical perspective, this is the most cost-effective approach because it saves you the most money on interest over time.
• The Debt Snowball: With this method, you focus on paying off the smallest debt balances first, regardless of the interest rate. Once the smallest debt is gone, you “roll” that payment amount into the next-smallest debt.
The power of the snowball method is counter-intuitive but profound. While it might lead to paying more in total interest, it provides quick wins that build motivation. The Debt Avalanche is for the pure optimizer who is motivated by math and long-term savings. The Debt Snowball is for the momentum-seeker who needs the psychological fuel of quick, tangible victories to stay in the fight.
4. An ‘Emergency’ Isn’t a Possibility, It’s an Inevitability
Life is unpredictable, and emergencies are not a matter of if, but when. You never know when you might face a job loss, a medical emergency, or a major car repair. Because life happens, an emergency fund is a non-negotiable foundation for financial security.
An emergency fund is a cash reserve set aside specifically for major, unexpected expenses. Most financial experts recommend saving three to six months of essential living expenses. This amount can feel daunting, which is why it’s often best to start smaller.
Aim to build a “starter emergency fund” of $1,000. That $1,000 is the difference between a sudden car repair being an annoying afternoon and a debt-inducing disaster that spirals for months. It’s the firewall between a surprise medical bill and having to sell something you value. This small, achievable goal provides a crucial safety net and prevents a single unexpected bill from forcing you into high-interest debt.
5. Your Most Powerful Financial Tool Isn’t Willpower—It’s Automation
Many people believe that financial success relies on constant discipline and willpower. However, a far more effective strategy is to build good habits that run on their own. The easiest way to do this is through automation.
Setting up automatic transfers from your checking account to your savings or investment accounts ensures you “pay yourself first.” The money is moved before you even have a chance to count it as spending money, making saving effortless. Automating your bill payments is just as powerful, helping you avoid costly late fees and protecting your credit score.
This is so powerful because it bypasses your brain’s weakest link: willpower. Financial success isn’t about having more discipline; it’s about needing less of it. Automation removes the daily choice to save, eliminating decision fatigue and making your financial goals the default outcome, not a daily struggle.
6. Your Employer Might Be Offering You Free Money
One of the most valuable and frequently overlooked financial assets is an employer’s 401(k) matching benefit. If your company offers this, you should take full advantage of it.
This benefit is, quite simply, free money. Many companies will match your contributions to a retirement account up to a certain percentage of your salary. Think of it this way: if you earn 60,000andyouremployermatchesupto53,000), failing to contribute that 5% is the equivalent of looking your boss in the eye and turning down a $3,000 annual raise. It’s a guaranteed 100% return on your investment you can’t get anywhere else.
Beyond the 401(k) match, be sure to research all the benefits available from your employer. You may have access to other perks that can lead to serious savings, such as discounted gym memberships or covered insurance costs.
7. Your Financial Plan Is a Garden, Not a Sculpture
It’s tempting to adopt a “set it and forget it” mindset with your finances, but a successful financial plan is a living document, not a stone sculpture carved once and left alone. Your financial picture is ever-evolving, and your plan must adapt with it.
Major life events like getting married, having children, buying a home, or changing jobs all require you to re-evaluate your strategies. Because of this, it’s critical to schedule regular financial check-ins. A good starting point is to review your finances annually. During this review, you should assess your budget, monitor your progress toward your goals, re-evaluate your investment allocation, and update your insurance policies.
Just like a garden, your financial plan needs regular tending, adjustments, and care to thrive. Consistent monitoring ensures it continues to align with your life and keeps you on the path toward your goals.
——————————————————————————–
Building financial security is not about some hidden secret; it’s about getting a grip on your habits and making a plan you can stick to. It requires understanding where your money goes, aligning your spending with your values, and creating systems that support your long-term goals. As financial expert Dave Ramsey says, it comes down to a simple choice:
You will either manage money or the lack of it will always manage you.
What is the one small change you can make today to start managing your money, instead of letting it manage you?
——————————————————————
Your First Map to Financial Freedom: A Guide for Young Adults
Your First Map to Financial Freedom: A Guide for Young Adults
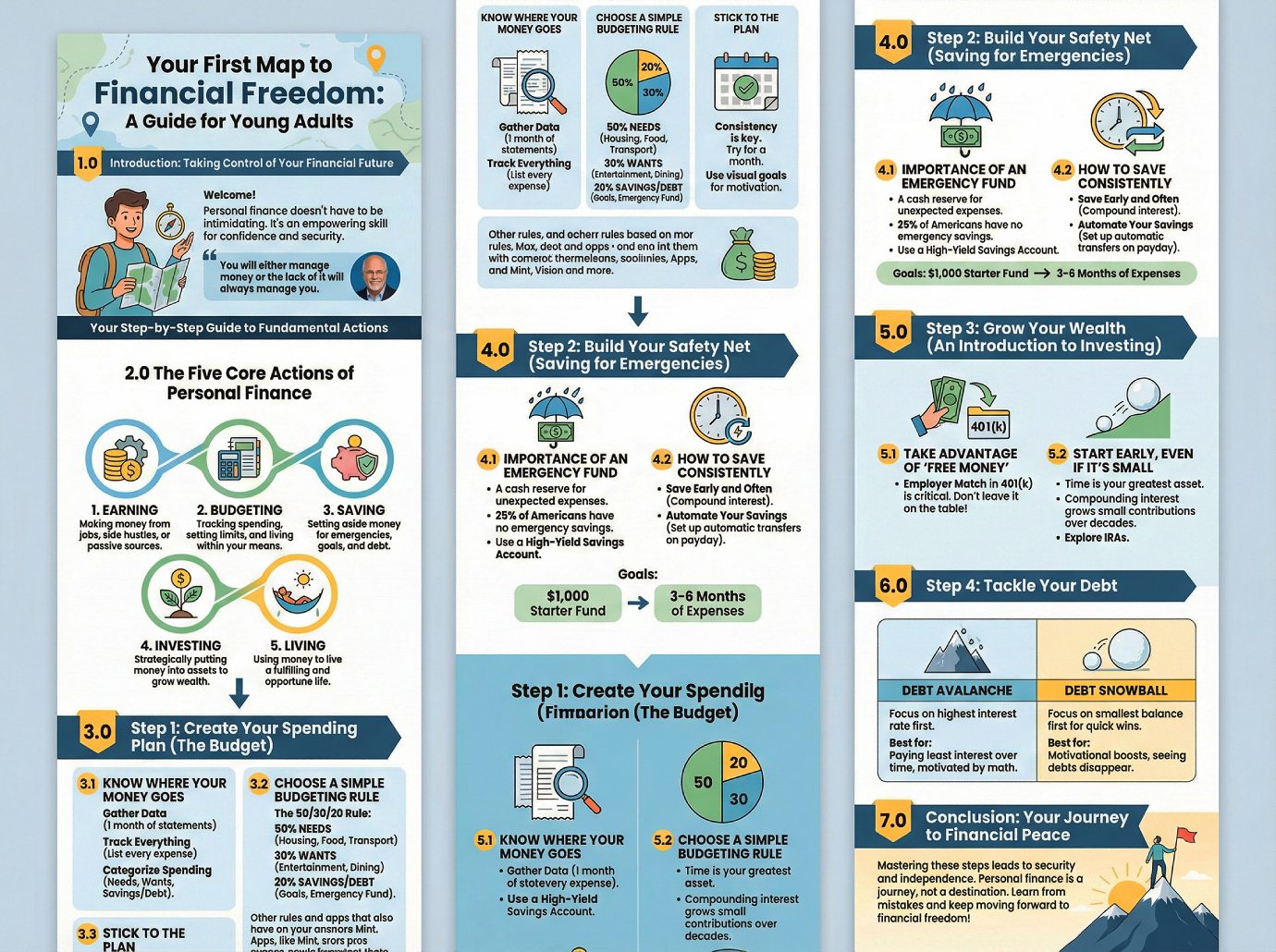
1.0 Introduction: Taking Control of Your Financial Future
Welcome! If the topic of personal finance feels intimidating, stressful, or just plain confusing, you’re not alone. For many people, money management is a subject accompanied by a feeling of apprehension. But here’s the good news: learning to handle your money is not a restrictive chore. It’s one of the most empowering skills you can develop, building a foundation for confidence, security, and a more fulfilling life.
Financial expert Dave Ramsey put it best:
“You will either manage money or the lack of it will always manage you.”
This article is designed to be your first map on this journey. Its purpose is to provide a clear, step-by-step guide to the fundamental actions of personal finance, tailored for a young adult who is just getting started.
Let’s begin by breaking down the core building blocks you’ll need to master.
2.0 The Five Core Actions of Personal Finance
Personal finance can seem complex, but at its heart, it boils down to just a handful of core actions. Understanding these concepts is the first step toward taking control.
• Earning: This is the process of making money, whether from a full-time job, part-time roles, or passive sources like real estate or dividend income.
• Budgeting: This involves tracking your spending habits and setting limits. The goal is to reduce your cash outflow, grow your financial confidence, and live a sustainable lifestyle.
• Saving: This is the act of setting money aside to protect against emergencies, pay off debt, and accumulate wealth for your goals.
• Investing: This means strategically putting your money into assets to grow your wealth or generate additional income for the future.
• Living: Don’t forget the “personal” side of personal finance. Ultimately, managing your money well should empower you to live a more fulfilling and opportune life.
Now that you understand these foundational concepts, let’s dive into the first and most critical practical step: creating your budget.
3.0 Step 1: Create Your Spending Plan (The Budget)
A budget is the foundational tool for managing your money. It’s a plan that helps you live within your means, take control of your spending, and achieve your financial goals. Here’s how you can create one in three simple sub-steps.
3.1 Know Where Your Money Goes
Before you can make a plan for the future, you need a clear picture of your present. It’s time to play detective with your own finances.
1. Gather Your Data: For one full month, collect all your financial documents. This includes bank statements, credit card statements, utility bills, and any records from electronic payment apps like Venmo or PayPal.
2. Track Everything: Create a simple spreadsheet or use a notebook to list every single expense.
3. Categorize Your Spending: As you list your expenses, group them into categories. A simple way to start is by labeling them as Needs (rent, groceries), Wants (entertainment, dining out), or Savings/Debt (payments, retirement contributions). This will show you exactly where the bulk of your money is going.
3.2 Choose a Simple Budgeting Rule
A budget doesn’t have to be complicated. A popular and easy-to-understand framework for beginners is the 50/30/20 rule, which divides your after-tax income into three main buckets.
| Category | Percentage | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Needs | 50% | Covers essential expenses like housing, utilities, food, and transportation. |
| Wants | 30% | For non-essential lifestyle purchases like entertainment, dining out, and hobbies. |
| Savings/Debt | 20% | Allocated to saving for goals, building an emergency fund, and paying off debt. |
Of course, the 50/30/20 rule is just one popular method. Others, like the 70/20/10 rule (70% expenses, 20% savings, 10% debt), are also great starting points. If a manual spreadsheet isn’t for you, explore budgeting apps like Mint or Quicken that can help automate the process.
3.3 Stick to the Plan
The key to a successful budget is consistency. Once you’ve created your spending plan, give it a try for at least a month to see if it works for you. To stay motivated, financial expert Patrice Washington recommends that you “surround yourself with visual representations” of your goals. If you’re saving for a trip, put up pictures of your destination to keep your goal fresh in your mind.
This discipline is more than just a habit; it’s the foundation for your financial security, which begins with building a powerful safety net.
4.0 Step 2: Build Your Safety Net (Saving for Emergencies)
Saving is your defense against life’s unexpected events. Having a dedicated savings fund allows you to handle financial curveballs without having to go into debt.
4.1 The Importance of an Emergency Fund
An emergency fund is a cash reserve set aside for major, unexpected expenses, such as a sudden job loss, a medical emergency, or a major car repair. Its importance cannot be overstated. A recent survey of 1,000 Americans found that 25% of respondents have no emergency savings at all, leaving them vulnerable to financial stress.
To make this safety net as effective as possible, be sure to keep these funds in a high-yield savings account. This allows your money to grow through compound interest while still being accessible when you need it.
• Start with a $1,000 Starter Fund: This initial cushion turns a potential crisis into a manageable inconvenience.
• Build Toward 3-6 Months of Expenses: This provides a robust safety net against more significant life events, like a job loss.
4.2 How to Save Consistently
The most effective way to build your savings is to make it a regular, automated habit.
• Save Early and Often: This simple principle is powerful because it allows your money to grow by earning interest. The sooner you start saving, the more time your money has to work for you.
• Automate Your Savings: Set up an automatic transfer from your checking account to your savings account for every payday. By moving the money right away, it disappears “before you can count it as spending money,” making it effortless to save consistently.
Once you have a safety net in place, you can move on to the next level of financial growth: investing for your future.
5.0 Step 3: Grow Your Wealth (An Introduction to Investing)
While saving protects you from emergencies, investing is the primary way to build long-term wealth and reach major goals like buying a home or retiring comfortably.
5.1 Take Advantage of “Free Money”
If you have a job, one of the easiest and most powerful ways to start investing is through an employer-sponsored retirement plan, like a 401(k). Many companies offer to match your contributions up to a certain percentage. This is a critical benefit you should never ignore.
If your employer matches your contributions up to 3%, contributing that amount gives you an immediate 100% return on your investment. It is “free money,” and leaving it on the table is one of the biggest financial mistakes you can make.
5.2 Start Early, Even if It’s Small
When it comes to investing, time is your greatest asset. The sooner you start, the more time your money has to grow through the power of compounding.
• Even small, regular contributions can grow into a significant sum over several decades.
• Beyond a 401(k), an Individual Retirement Account (IRA) is another powerful tool for long-term saving that offers unique tax advantages.
While saving and investing are about moving forward, many young adults must first deal with an obstacle holding them back: existing debt.
6.0 Step 4: Tackle Your Debt
Managing and eliminating debt is a critical step on the path to financial freedom. Once you’ve organized your debts, you can choose a repayment strategy that works best for you. The two most common methods are the Debt Avalanche and the Debt Snowball.
| Strategy | How It Works | Best For… |
|---|---|---|
| Debt Avalanche | You focus on paying off the debt with the highest interest rate first, while making minimum payments on others. | The person who wants to pay the least amount of interest over time and is motivated by math and efficiency. |
| Debt Snowball | You focus on paying off the smallest debt balance first, regardless of the interest rate, to get quick wins. | The person who needs motivational boosts and gains confidence from seeing individual debts disappear completely. |
With a strategy for your past (debt) and your present (budget), you now have all the tools you need to build a peaceful and prosperous financial future.
7.0 Conclusion: Your Journey to Financial Peace
Building a strong financial future comes down to mastering a few key actions. By creating a budget, building an emergency fund, starting to invest for the long term, and making a plan to tackle your debt, you are taking powerful steps toward security and independence.
Remember that personal finance is a journey, not a destination. You will make mistakes along the way, and that’s perfectly okay.
Remember, the important thing is to acknowledge mistakes and learn from the process. If you can do that, you’ll be well on your way to financial freedom.
——————————————————————
Personal Finance Strategy and Management: A Synthesis
Personal Finance Strategy and Management: A Synthesis
Executive Summary
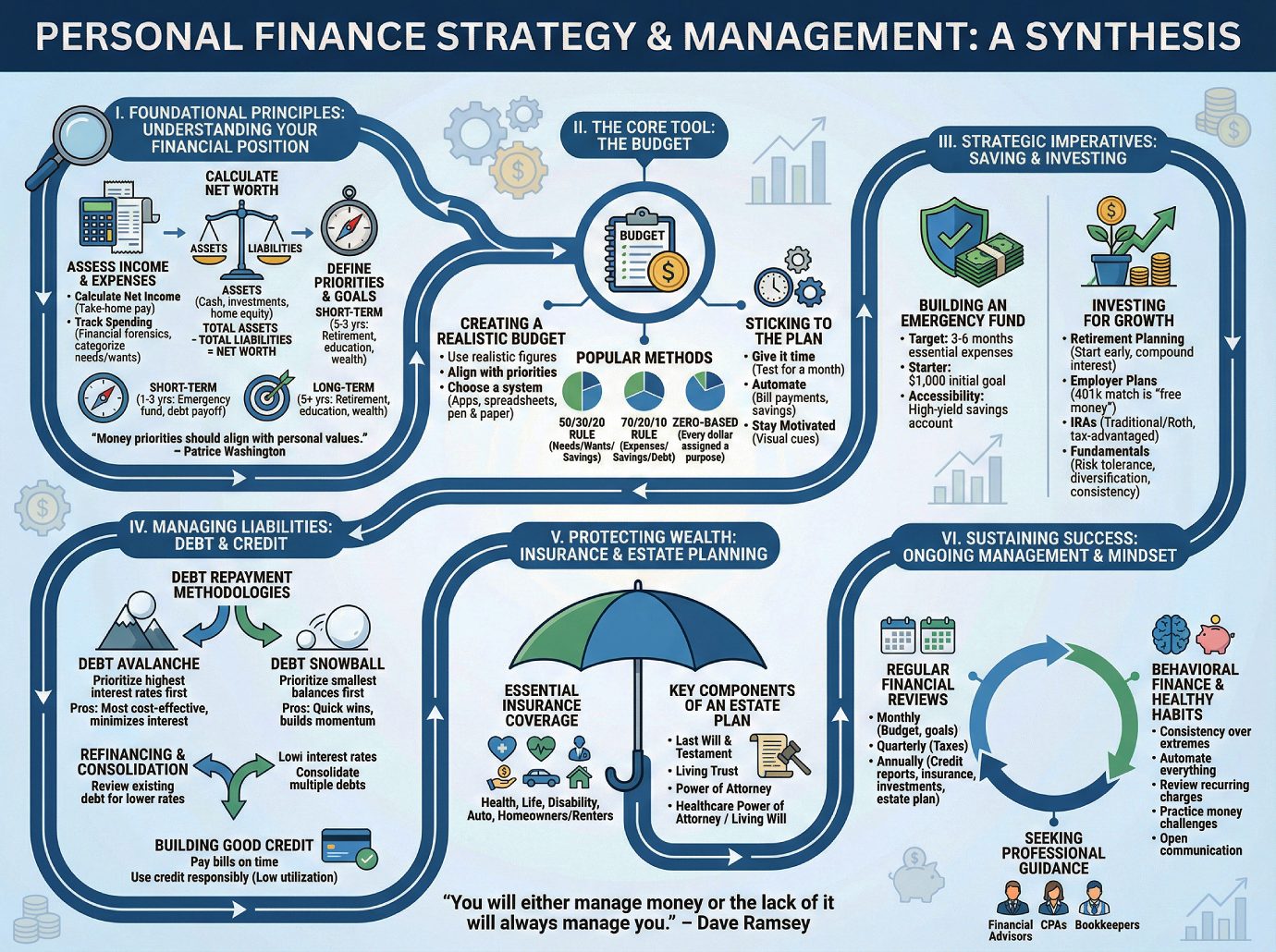
Effective personal financial management is a critical, lifelong discipline essential for achieving financial security and peace of mind. A comprehensive analysis of financial guidance reveals a consistent, multi-stage framework for success. The process begins with a foundational understanding of one’s complete financial picture—meticulously tracking all income sources and expenditures to calculate net worth and define personal priorities.
The primary tool for financial control is a realistic, consistently maintained budget, which aligns spending habits with strategic goals. Key among these goals is the creation of a robust savings plan, prioritizing an accessible emergency fund equivalent to three to six months of living expenses to buffer against unexpected events. Concurrently, a strategic approach to debt reduction, utilizing methods such as the “avalanche” or “snowball” techniques, is vital for freeing up capital and improving financial health.
For long-term wealth creation, early and consistent investment is paramount, particularly through tax-advantaged retirement vehicles like 401(k)s and IRAs, and capitalizing on employer matching programs. Finally, wealth must be protected through adequate insurance coverage and comprehensive estate planning. This entire process is dynamic; it requires regular reviews and adjustments to adapt to life events and evolving goals, ensuring sustained financial well-being. As financial expert Dave Ramsey states, “You will either manage money or the lack of it will always manage you.”
——————————————————————————–
I. Foundational Principles: Understanding Your Financial Position
Before any financial plan can be effective, a thorough and honest assessment of one’s current financial situation is required. This stage is about gathering data to create an accurate snapshot of financial health, which serves as the baseline for all subsequent planning and decision-making.
Assessing Income and Expenses
The first step is to gain a clear understanding of cash flow by determining monthly income and tracking all expenditures.
• Calculate Monthly Income: Determine total monthly take-home pay (net income) after taxes. This should include income from primary employment, side gigs (freelance work, ad revenue), and any other regular sources. For those with variable income, such as freelancers, an average or estimated monthly income should be calculated.
• Track Spending: Conduct a “financial forensics” on personal spending habits. This involves collecting and analyzing at least one month’s worth of financial records, including:
◦ Credit card and bank statements
◦ Housing and utility bills
◦ Records of electronic payments (Venmo, PayPal)
◦ ATM withdrawal records
• Categorize Expenses: As expenses are tallied, they should be grouped into categories. This can be a simple breakdown of “needs,” “wants,” and “savings/debt,” or a more detailed list including categories like housing, transportation, food, entertainment, and travel. This categorization reveals where the bulk of income is directed.
Calculating Net Worth
Understanding net worth provides a holistic view of one’s financial standing at a specific point in time. It should be calculated annually to track progress.
| Component | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Assets | Everything owned that has monetary value. | Cash, checking/savings accounts, investments, home equity, vehicles. |
| Liabilities | All outstanding debts and financial obligations owed to others. | Mortgages, car loans, student loans, credit card balances. |
| Net Worth | Total Assets – Total Liabilities | A positive figure indicates owning more than is owed. |
Defining Financial Priorities and Goals
With a clear financial picture, the next step is to define priorities and set specific, measurable goals. This crucial step provides motivation and direction for a financial plan.
• Align with Personal Values: As personal finance authority Patrice Washington advises, money priorities should align with personal values. “The largest categories should reflect what matters most to you,” whether that is travel, fitness, or family.
• Set Tangible Goals: Financial goals should be specific, with numbers and dates attached. They can be broken down into two main categories:
◦ Short-Term Goals (1-3 years): Building an emergency fund, paying off high-interest credit card debt, saving for a vacation, or making a down payment on a vehicle.
◦ Long-Term Goals (5+ years): Saving for a home down payment, funding a child’s education, starting a business, building wealth, or planning for retirement.
II. The Core Tool: The Budget
A budget is the central planning document that translates financial goals into an actionable spending plan. It is not merely a restrictive tool but a guide for allocating resources effectively to achieve desired outcomes.
Creating a Realistic Budget
An effective budget must be based on the accurate income and expense data gathered in the foundational stage.
1. Use Realistic Figures: The budget should reflect finances as they currently are, not as one wishes them to be.
2. Align with Priorities: The plan should direct spending toward the priorities identified in the goal-setting phase. For example, if establishing an emergency fund is the top priority, the budget must allocate funds to a dedicated savings account by reducing spending in lower-priority areas.
3. Choose a System: Select a budgeting system that is easy to maintain. Options include:
◦ Simple spreadsheets
◦ Dedicated budgeting apps (e.g., Mint, You Need a Budget (YNAB), Quicken, Goodbudget)
◦ Pen and paper
Popular Budgeting Methods
Several established frameworks can guide the creation of a budget.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| 50/30/20 Rule | 50% of take-home pay is allocated to Needs (housing, utilities, groceries). 30% is allocated to Wants (entertainment, dining out). 20% is allocated to Savings and Debt Repayment. |
| 70/20/10 Rule | 70% of take-home pay is for Expenses. 20% is for Savings. 10% is for Debt Repayment. |
| Zero-Based | Every dollar of income is assigned a specific purpose (spending, saving, debt), leaving a balance of zero. |
Sticking to the Plan
Consistency is the key to a successful budget.
• Give it Time: A new budget should be tested for at least one full month to determine its effectiveness and sustainability.
• Automate: Set up automatic bill payments and savings transfers. This ensures priorities are met before money can be spent elsewhere.
• Stay Motivated: Use visual cues to maintain focus. Patrice Washington recommends surrounding oneself with “visual representations” of goals, such as pictures of a dream vacation destination.
III. Strategic Imperatives: Saving and Investing
Once a budget is in place, the focus shifts to building financial security and growing wealth through disciplined saving and strategic investing.
Building an Emergency Fund
An emergency fund is a liquid cash reserve for major, unexpected expenses (e.g., job loss, medical emergencies, major car repairs). It is a critical financial safety net.
• Target Amount: The standard recommendation is to save three to six months of essential living expenses.
• Starter Fund: For those starting out, a more achievable initial goal is a $1,000 starter emergency fund. A recent survey noted that 25% of respondents had no emergency savings at all.
• Accessibility: These funds should be kept in a high-yield savings account where they are easily accessible but separate from regular checking accounts to avoid casual spending.
Saving for Goals
Beyond emergencies, savings should be directed toward specific short-term and long-term goals. Using separate, dedicated savings accounts for different goals (e.g., “Vacation Fund,” “New Car Fund”) can improve organization and motivation.
Retirement Planning and Investment Strategies
Saving for retirement should begin as early as possible to maximize the power of compound interest.
• Employer-Sponsored Plans (401k): If an employer offers a 401(k) matching program, contributing enough to receive the full match is essential. This is often described as “free money.”
• Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs): IRAs (Traditional or Roth) are powerful, tax-advantaged tools for retirement savings, available to those with or without an employer plan.
• Investing Fundamentals:
◦ Risk Tolerance: Understand your personal comfort level with market fluctuations.
◦ Diversification: Spread investments across various asset classes (stocks, bonds) to manage risk.
◦ Consistency: Invest regularly, even small amounts. Don’t try to time the market by jumping in and out.
◦ Accessibility: Financial apps and robo-advisors like Wealthfront and Betterment have made investing more accessible for beginners.
IV. Managing Liabilities: Debt and Credit
Effectively managing and reducing debt is crucial for financial progress, as high-interest payments can significantly hinder the ability to save and invest.
Debt Repayment Methodologies
Two primary strategies exist for paying down debt. The choice depends on whether mathematical efficiency or psychological motivation is a higher priority.
| Method | Approach | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Debt Avalanche | Prioritize paying off debts with the highest interest rates first, while making minimum payments on others. | Most cost-effective; minimizes total interest paid. | May take longer to see the first debt eliminated. |
| Debt Snowball | Prioritize paying off debts with the smallest balances first, regardless of interest rate. | Provides quick wins and builds momentum/confidence. | May result in paying more total interest over time. |
Refinancing and Consolidation
Regularly review existing debt to identify opportunities for savings. This can include:
• Refinancing mortgages, auto loans, or student loans to secure a lower interest rate.
• Consolidating multiple debts into a single personal loan with a lower interest rate.
• Transferring high-interest credit card balances to a card with a lower introductory or promotional interest rate.
Building and Maintaining Good Credit
A strong credit history is essential for accessing future loans at favorable rates. Responsible financial habits are key.
• Pay Bills on Time: This is a fundamental component of a good credit score.
• Use Credit Responsibly: Open credit cards and use them responsibly by making on-time payments and maintaining a low credit utilization rate.
V. Protecting Wealth: Insurance and Estate Planning
Building wealth is only part of the equation; protecting it from unforeseen events is equally important. This involves having adequate insurance and a comprehensive estate plan.
Essential Insurance Coverage
Insurance acts as a safeguard against catastrophic financial loss. Key types include:
• Health Insurance: Protects against high medical costs.
• Life Insurance: Provides financial support for dependents.
• Disability Income Insurance: Replaces a portion of income if one is unable to work due to illness or injury.
• Auto Insurance: Covers expenses related to vehicle accidents.
• Homeowners or Renters Insurance: Protects property and personal belongings.
Key Components of an Estate Plan
Estate planning ensures assets are distributed according to one’s wishes and that personal affairs are handled in case of incapacitation.
• Last Will and Testament: A legal document outlining how assets should be distributed and naming guardians for minor children.
• Living Trust: Can help heirs avoid the potentially lengthy and costly probate process.
• Power of Attorney: Designates a trusted individual to make financial decisions on your behalf if you become unable to do so.
• Healthcare Power of Attorney / Living Will: Outlines preferences for medical treatment and designates someone to make healthcare decisions on your behalf.
VI. Sustaining Success: Ongoing Management and Mindset
Personal finance is a dynamic, ongoing process that requires regular attention and a disciplined mindset.
The Importance of Regular Financial Reviews
A “set it and forget it” mindset does not work for personal finance. Schedule regular check-ins to stay on track.
• Monthly: Review the budget and track progress toward goals.
• Quarterly: Check on tax deadlines if applicable.
• Annually:
◦ Review credit reports from all three major bureaus (Equifax, Experian, TransUnion).
◦ Re-evaluate insurance coverage.
◦ Review investment portfolio and rebalance if necessary.
◦ Meet with a financial professional.
◦ Update estate planning documents after major life events (marriage, birth of a child, etc.).
Behavioral Finance and Healthy Habits
Mindset and behavior are as important as the numbers.
• Consistency over Extremes: Drastic “crash diet” approaches to finance are often unsustainable. Small, consistent changes, like reducing spending by 10%, are more effective.
• Automate Everything: Automate savings, investments, and bill payments to remove friction and the temptation to spend.
• Review Recurring Charges: Scrutinize bank statements for subscriptions and memberships that are no longer used. Research found that forgotten subscriptions cost consumers £1.6 billion a year.
• Practice Money Challenges: Short-term challenges like a “no-spend month” or the “1p challenge” (saving an additional penny each day) can build savings habits in an engaging way.
• Open Communication: For those with partners, regular, open conversations about money are crucial for aligning goals and building a shared financial future.
Seeking Professional Guidance
Financial matters can be complex. Working with professionals can provide up-to-date, personalized guidance. Consider consulting with:
• Financial Advisors: For comprehensive financial planning and investment management.
• Certified Public Accountants (CPAs): For tax planning and preparation.
• Bookkeepers: For managing day-to-day business finances.
